Welcome to your personalized skincare routine! This guide is designed to help you care for your skin daily, weekly, and monthly, with specific recommendations for managing acne, eczema, and premature aging. Remember, consistency is key to seeing results, and this routine is here to support you every step of the way.
Guided Skincare Education
Each chapter provides in-depth explanations of skincare products tailored to different skin concerns such as acne, eczema, hyperpigmentation, and aging. Whether you’re dealing with breakouts, dryness, or signs of aging, you’ll learn exactly how to care for your skin with the right products, routines, and treatments.
What You'll Learn:
- How to choose and use cleansers, toners, serums, moisturizers, and sunscreens that are perfect for your skin type.
- The importance of consistency in skincare and how to structure an effective routine.
- Advanced skincare tips such as the use of night creams, exfoliants, and facial masks to enhance your regimen.
How to Use It:
- Read through each product section to understand what ingredients work best for your skin concerns.
- Take notes on which products and techniques resonate with you, and incorporate them into your daily and weekly routines.
Your skincare journey is personal, and healing takes time. This workbook is your supportive guide, helping you understand your skin and empowering you to cultivate self-love, patience, and consistency. As you engage with these practices, you’ll see not only your skin transform but also a shift in your overall sense of well-being.
UNDERSTANDING YOUR SKIN
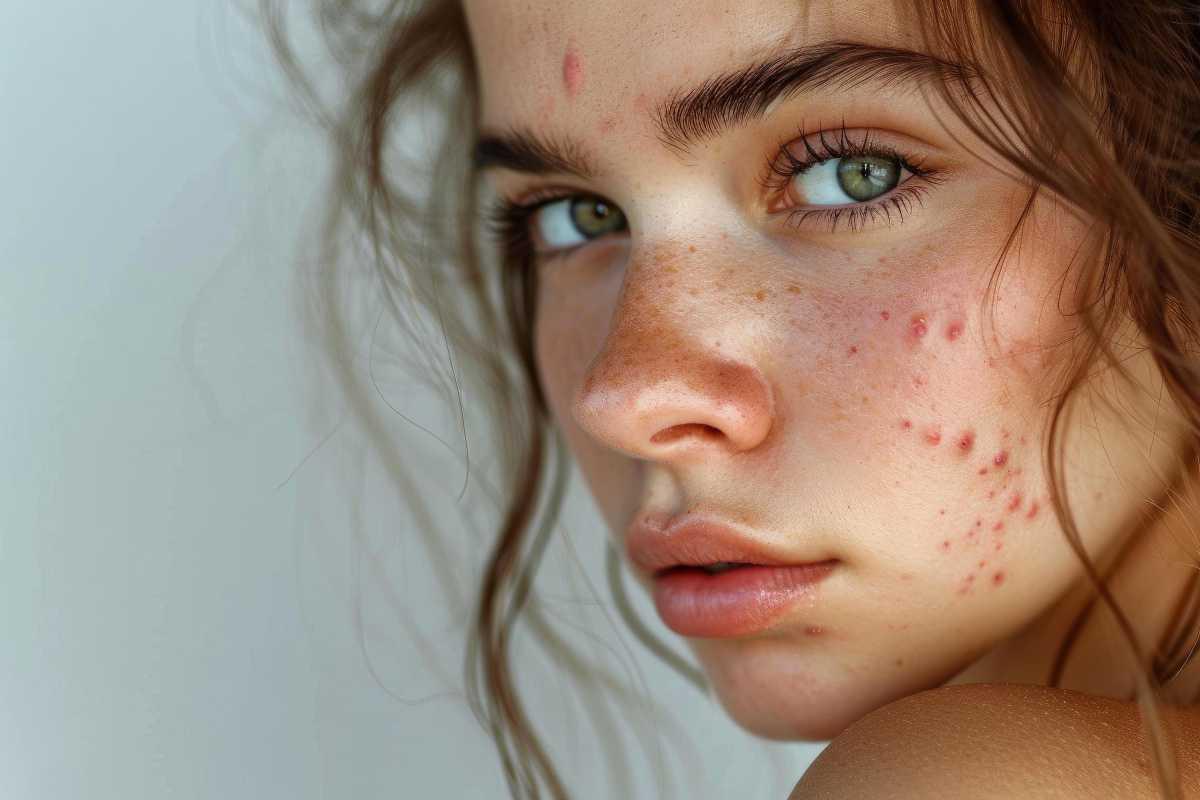
ACNE-PRONE SKIN
Acne-prone skin is often a source of frustration and self-consciousness. It’s characterized by frequent breakouts, including blackheads, whiteheads, and possibly inflamed cystic acne, which can be painful and leave scars if not treated properly. This skin type is usually associated with excess oil production, particularly in the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin), where the sebaceous glands are more active.
However, it’s important to note that not all acne-prone skin is oily—some individuals may experience acne alongside dryness or sensitivity, making treatment more complex. For acne-prone skin, the use of non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) products is crucial. It's also sensitive to certain ingredients, like heavy oils, alcohol, or harsh exfoliants, which can aggravate breakouts and lead to further irritation.
Common triggers for acne include hormonal fluctuations, stress, diet (such as high sugar or dairy intake), and the use of inappropriate skincare products. It’s essential to adopt a skincare routine that balances oil production without over-drying the skin, gently exfoliates to prevent clogged pores, and soothes inflammation to promote healing.
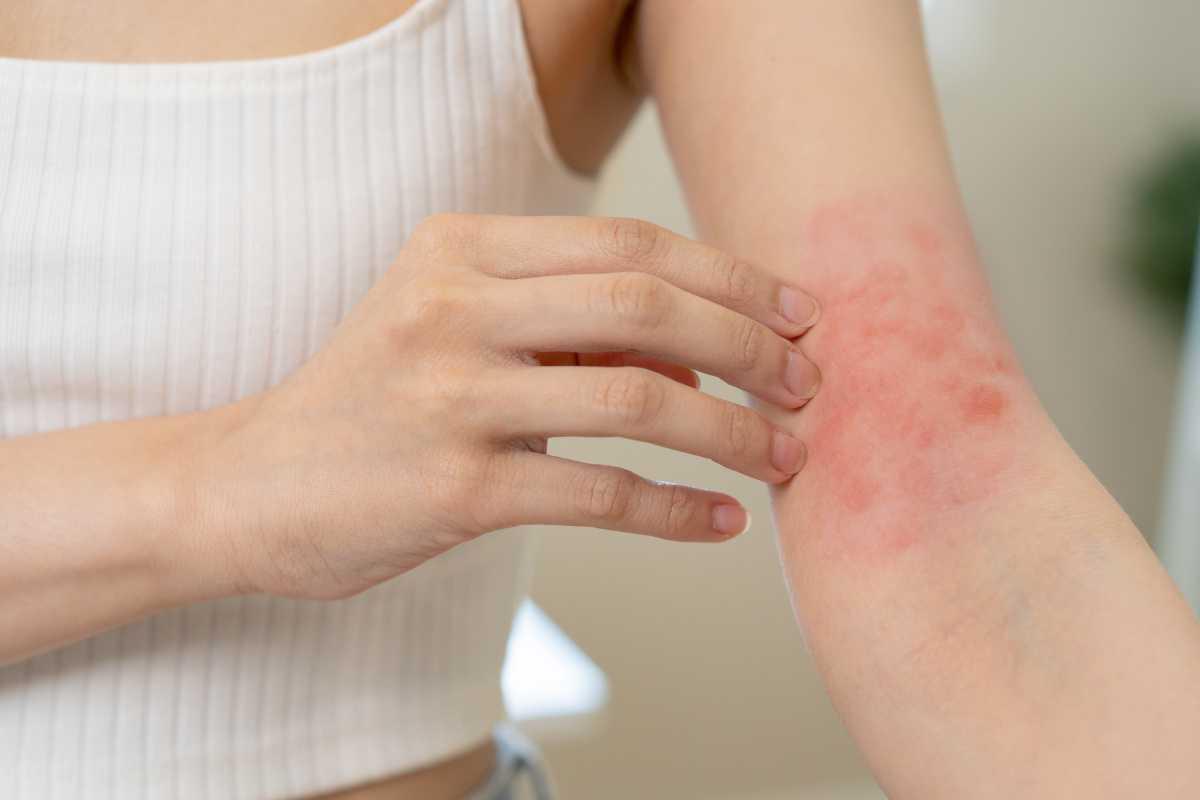
ECZEMA-PRONE SKIN
Eczema-prone skin requires delicate care, as it is typically dry, sensitive, and prone to flare-ups of red, itchy patches. This condition, also known as atopic dermatitis, is often triggered by environmental factors such as cold weather, pollution, or harsh soaps and detergents. Stress and allergens, including certain foods or fabrics, can also exacerbate symptoms.
The skin barrier in eczema-prone individuals is often compromised, meaning it loses moisture more quickly and is more susceptible to irritants. This makes it crucial to use products that are hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and designed to reinforce the skin's natural barrier function. Ingredients such as ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and oatmeal are beneficial for their hydrating and soothing properties.
Eczema-prone skin benefits from a routine that emphasizes moisture retention and barrier repair. Gentle, non-foaming cleansers and rich, emollient moisturizers are key components of such a routine. It's also helpful to incorporate anti-inflammatory ingredients to calm flare-ups and reduce the itching and redness associated with eczema.
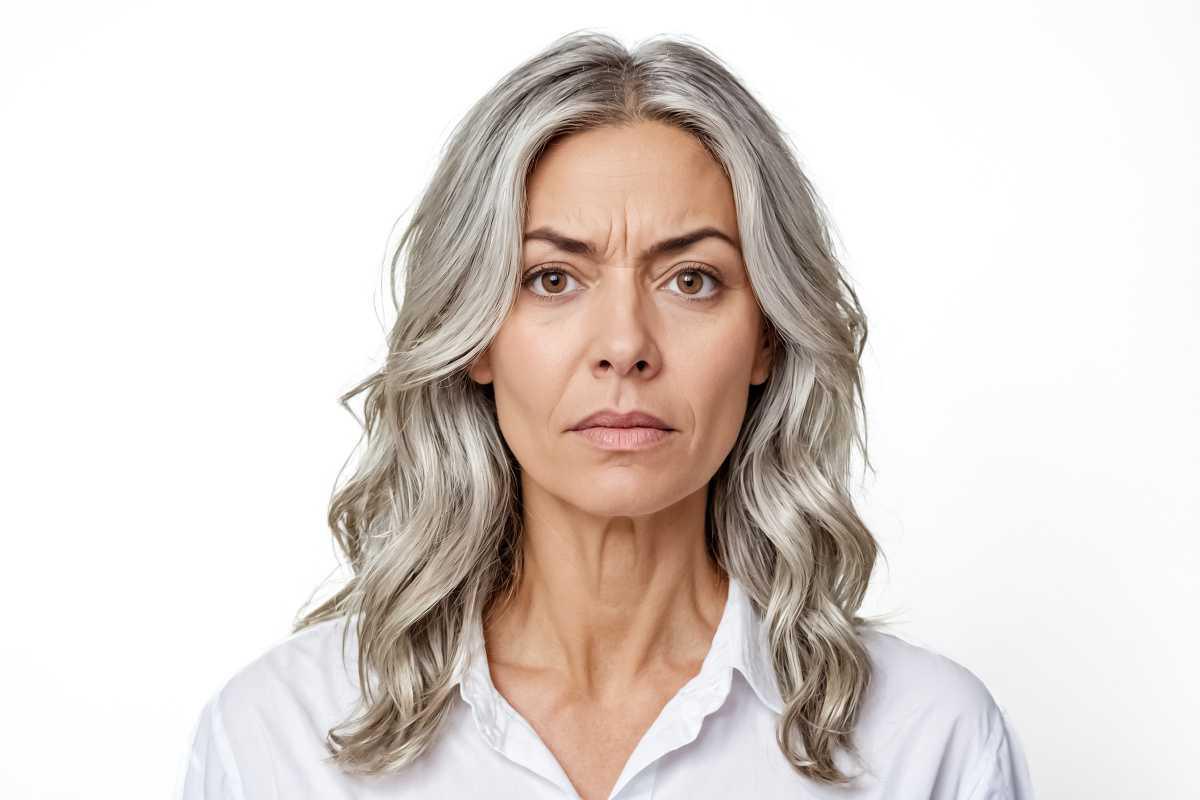
PREMATURE AGING SKIN
Premature aging skin often manifests as fine lines, wrinkles, a loss of elasticity, and an uneven skin tone. These signs are typically caused by a combination of factors, including prolonged sun exposure, which accelerates the breakdown of collagen and elastin, and stress, which can lead to an increase in cortisol levels that degrade skin structure.
Other contributing factors include poor hydration, smoking, pollution, and even repetitive facial expressions that, over time, cause lines to become more pronounced. For those with premature aging skin, it’s essential to protect the skin from further damage while also working to repair existing signs of aging.
A skincare routine for premature aging should focus on hydration, collagen stimulation, and sun protection. Key ingredients include antioxidants (such as vitamin C), retinoids, hyaluronic acid, and peptides, which help to boost collagen production, plump the skin, and smooth out fine lines. Daily use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen is non-negotiable, as it helps prevent further UV-induced damage.
HYPERPIGMENTATION
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by darkened areas or patches on the skin. These patches result from an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Hyperpigmentation can be caused by various factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or from birth control pills), acne scars, and inflammation from skin injuries.
Individuals with hyperpigmentation often struggle with uneven skin tone and dark spots that can be difficult to treat. To address hyperpigmentation, it’s crucial to protect the skin from further sun damage by using a high-SPF sunscreen daily. Treatment options often include ingredients that inhibit melanin production, such as vitamin C, niacinamide, and alpha arbutin. Exfoliating agents like AHAs (alpha hydroxy acids) and BHAs (beta hydroxy acids) can help to fade existing dark spots by encouraging cell turnover and the shedding of pigmented skin cells.
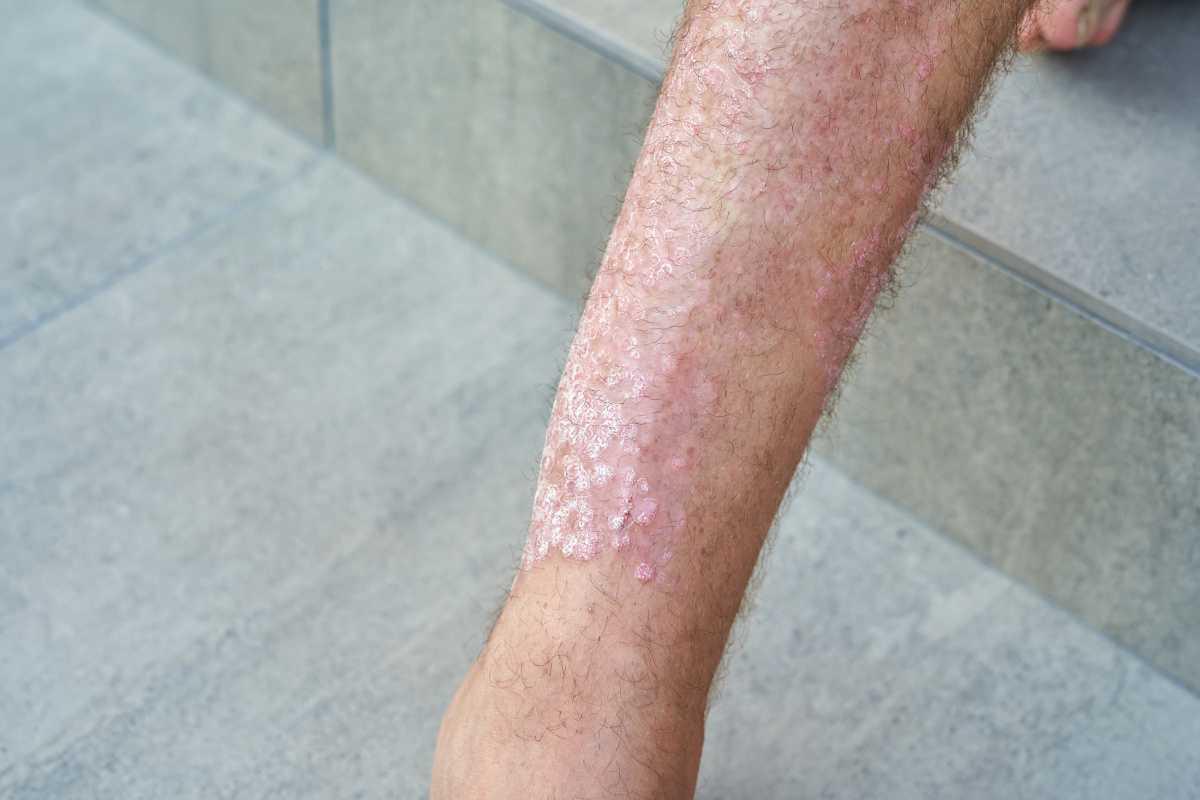
PSORIASIS
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to multiply up to ten times faster than normal. This leads to a buildup of cells on the skin's surface, forming thick, scaly patches that can be itchy, painful, and inflamed. These plaques often appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, but they can develop anywhere on the body.
Psoriasis-prone skin requires a skincare routine focused on reducing inflammation, soothing irritation, and maintaining moisture balance. It's important to use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and rich moisturizers to support the skin barrier. Ingredients such as salicylic acid, coal tar, and corticosteroids are commonly used in psoriasis treatments to reduce scaling and inflammation.
Managing stress is also crucial for those with psoriasis, as flare-ups can be triggered by emotional stress. Incorporating mindfulness practices into your skincare routine can help to manage stress and potentially reduce the frequency and severity of psoriasis flare-ups.
By understanding the specific needs of your skin—whether it’s acne-prone, eczema-prone, hyperpigmented, psoriasis-prone, or showing signs of premature aging—you can tailor your skincare routine to address these concerns effectively and holistically. This understanding forms the foundation for achieving healthier, more radiant skin that reflects your overall well-being.
✅ Scientific Citations for Skincare Concerns
Acne-Prone Skin
-
Sebum and Hormonal Influence: Acne is linked to increased sebum production and androgenic hormones. Source: Zaenglein, A. L., et al. (2016). "Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris." Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.037
-
Non-comedogenic Products & Diet: Topical treatments and dietary modifications (e.g., reduced dairy and sugar) may improve acne. Source: Baldwin, H. E. (2012). "The role of inflammation and the microbiome in acne." Dermatologic Clinics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2011.11.004
Eczema-Prone Skin (Atopic Dermatitis)
-
Skin Barrier & Moisturizers: Ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and emollients strengthen the barrier and improve symptoms. Source: Paller, A. S., et al. (2016). "New insights about epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis." Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.02.025
-
Triggers & Hypoallergenic Care: Avoiding fragrances, detergents, and allergens is essential. Source: Wollenberg, A., et al. (2018). "Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema." Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14888
Premature Aging
-
UV Exposure & Antioxidants: Sunscreen, retinoids, and antioxidants (e.g., vitamin C) can prevent and reverse aging signs. Source: Draelos, Z. D. (2010). "Cosmeceuticals for photoaging." Dermatologic Clinics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2010.03.006
-
Retinoids and Peptides: Topical retinoids increase collagen synthesis and improve elasticity. Source: Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). "Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging." Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2699641/
Hyperpigmentation
-
Vitamin C, Niacinamide, and AHAs: These ingredients inhibit melanin synthesis and improve skin tone. Source: Ando, H., et al. (2010). "Skin-lightening effects of topical niacinamide and other agents." Journal of Dermatological Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2009.12.004
-
Sun Protection: Sunscreen is critical to prevent hyperpigmentation from worsening. Source: Sheth, V. M., & Pandya, A. G. (2011). "Melasma: a comprehensive update." Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2010.07.004
Psoriasis-Prone Skin
-
Inflammatory Response & Topicals: Psoriasis is driven by immune dysregulation. Topical corticosteroids and salicylic acid reduce scaling and inflammation. Source: Armstrong, A. W., & Read, C. (2020). "Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis." JAMA. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.4006
-
Stress Management & Mindfulness: Stress exacerbates psoriasis. Mindfulness and lifestyle changes can reduce flare-ups. Source: Hughes, J. E., et al. (2020). "The impact of mindfulness-based interventions on psoriasis." British Journal of Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.18973